Current Trends in Bioinformatics and Genome Analysis
Go Back
Section - 1
Databases and tools in CADD
Various Databases:
1.Protein Data Bank (PDB)
http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/home/home.do
2.PubChem
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
3.DrugBank Version 5.0
https://www.drugbank.ca/
Protein Data Bank
Repository for 3D‐structural data of biological macromolecules.The structures can be obtained by different techniques, e.g. crystallography, electron microscopy, NMR.Data is freely accessible on the internet, e.g. www.rcsb.org . Key resource for structural biology – most journals require experimentally determined structures to be submiKed to the PDB before publication. . Each entry is reviewed by PDB staff and automatically checked for plausibility as of today there are 84846 structures in the PDB ‐ 82% solved by X‐ray
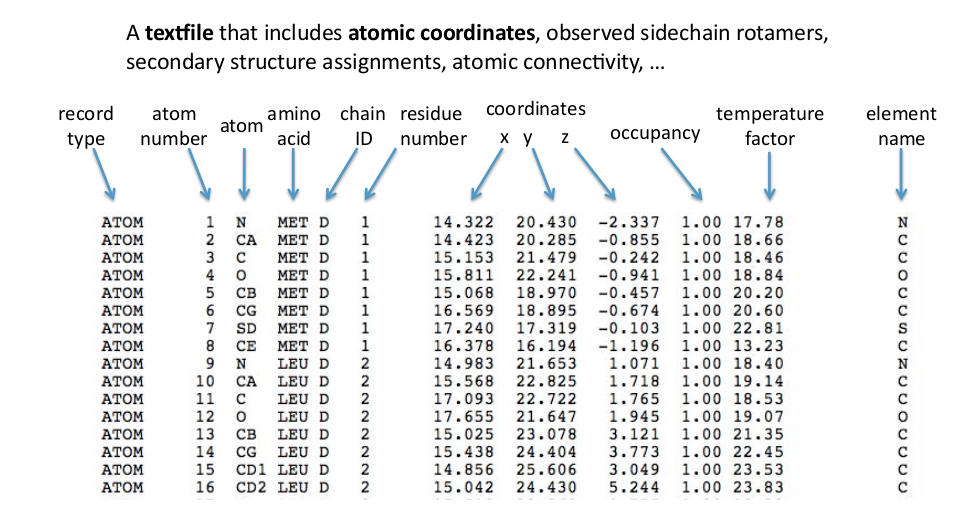
PDB format
PubChem
PubChem, released in 2004, provides information on the biological activities of small molecules. PubChem is organized as three linked databases within the NCBI's Entrez information retrieval system. These are PubChem Substance, PubChem Compound, and PubChem BioAssay. PubChem also provides a fast chemical structure similarity search tool.
DrugBank Version 5.0
PubChem, released in 2004, provides information on the biological activities of small molecules.
PubChem is organized as three linked databases within the NCBI's Entrez information retrieval system.
These are PubChem Substance, PubChem Compound, and PubChem BioAssay.
PubChem also provides a fast chemical structure similarity search tool.
DrugBank is a detailed database on small molecule and biotech drugs. Each drug entry ("DrugCard") extensive information on properties, structure, and biology (what the drug does in the body). Each drug can have 1 or more targets, enzymes, transporters, and carriers associated. Below is a quick definition list to get you started.
Small Molecule Drug - A drug from largely synthetic origins, typically under 1000 MW, however there are some exceptions (for example, Ivermectin)
Biotech Drug - Drugs which are peptide, protein or nucleic acid drugs
Target- A protein, macromolecule, nucleic acid, or small molecule to which a given drug binds, resulting in an alteration of the normal function of the bound molecule and a desirable therapeutic effect. Drug targets are most commonly proteins such as enzymes, ion channels, and receptors.
Enzyme - A protein which catalyzes chemical reactions involving the a given drug (substrate). Most drugs are metabolized by the Cytochrome P450 enzymes.
Transporter- A membrane bound protein which shuttles ions, small molecules or macromolecules across membranes, into cells or out of cells.
Carrier - A secreted protein which binds to drugs, carrying them to cell transporters, where they are moved into the cell. Drug carriers may be used in drug design to increase the effectiveness of drug delivery to the target sites of pharmacological actions.
Chemical Sketching
Chemical sketching allows us to draw chemical structures including organics, organometallics, polymers etc.
- Pubchem Sketcher ( https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/edit2/index.html)
- ChemDoodle ( https://web.chemdoodle.com/demos/sketcher/)




